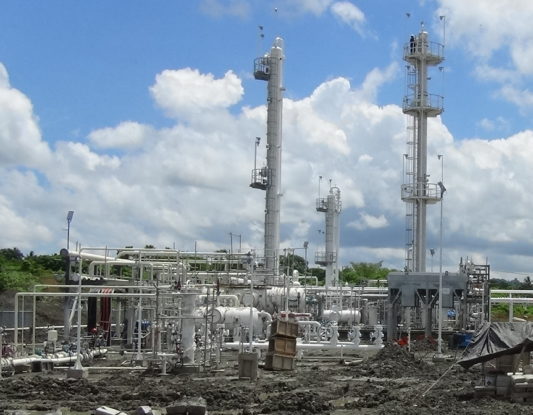
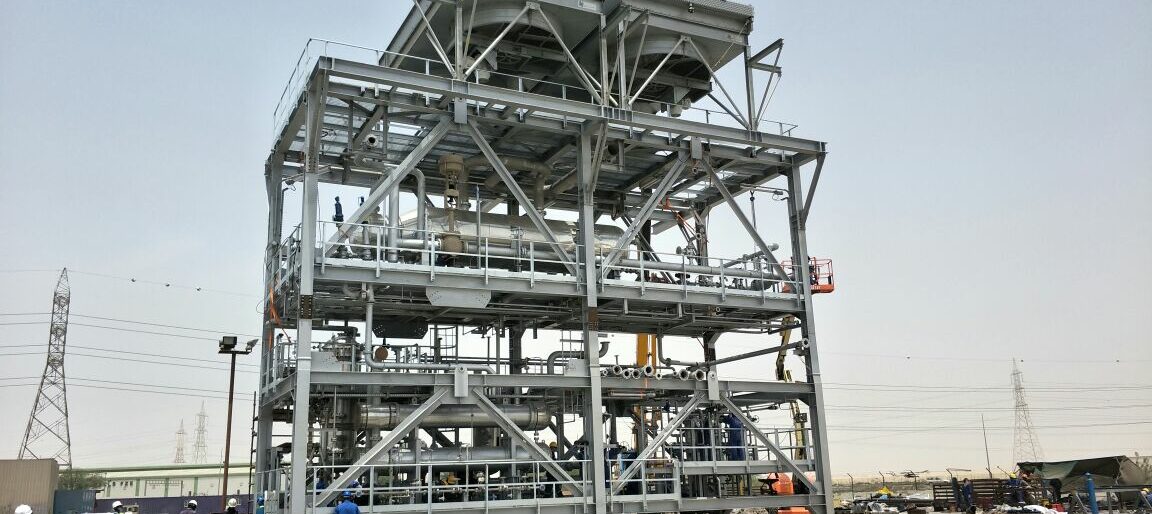
AMINE SELECTION CONSIDERATIONS
• Contaminant type and concentration in feed
• Treated product specification
• Requirements for selectivity
• Operating temperature and pressure
• Solvent capital and operating cost
• Associated fees for specialty amines
Primary Amines
• Low operating pressure systems
• Low solvent cost
• Susceptible to amine degradation
• Higher vaporization losses
• Non-selective for H2S over CO2
Secondary Amines
• More suitable for higher pressures
• Resistant to degradation by carbonyl sulphide (COS) and carbon disulphide (CS2)
• Lower energy requirements to regenerate
• Non-selective for H2S over CO2
• Lower reactivity of amine and H2S & CO2
• Requires increased amine circulation rates
Tertiary Amines
• Higher solution concentration
• Higher acid gas loading
• Resistant to degraded by COS and CS2
• Selective removal of H2S over CO2
• Lower energy requirements for regeneration
• Lower required solvent circulation
• Higher solvent costs and losses
Formulated Amines
• Customizable selectivity for component removal and slip
Physical Solvents
• Acid gas components are dissolved and absorbed in the solvent compared to chemical reactions with H2S and CO2 for amine solvents.
• Efficient for mercaptan removal
Hybrid Amines
• Combination of physical and chemical solvent properties
• Increased acid gas loading compared to pure solvents